Section 2 – Implement a Security Extension of a Layer 2 solution, given a network design and a set of requirements
QUESTION NO: 16
Refer to the exhibit. What will happen to traffic within VLAN 14 with a source address of 172.16.10.5?

A. The traffic will be forwarded to the router processor for further processing.
B. The traffic will be dropped.
C. The traffic will be forwarded to the TCAM for further processing.
D. The traffic will be forwarded without further processing.
Answer: B
Explanation:
VLAN maps, also known as VLAN ACLs or VACLs, can filter all traffic traversing a switch. VLAN maps can be configured on the switch to filter all packets that are routed into or out of a VLAN, or are bridged within a VLAN. VLAN maps are used strictly for security packet filtering. Unlike router ACLs, VLAN maps are not defined by direction (input or output).
To create a VLAN map and apply it to one or more VLANs, perform these steps: Create the standard or extended IP ACLs or named MAC extended ACLs to be applied to the VLAN. This access-list will select the traffic that will be either forwarded or dropped by the access-map. Only traffic matching the ‘permit’ condition in an access-list will be passed to the access-map for further processing. Enter the vlan access-map access-map-name [ sequence ] global configuration command to create a VLAN ACL map entry. Each access-map can have multiple entries. The order of these entries is determined by the sequence . If no sequence number is entered, accessmap entries are added with sequence numbers in increments of 10. In access map configuration mode, optionally enter an action forward or action drop . The default is to forward traffic. Also enter the match command to specify an IP packet or a non-IP packet (with only a known MAC address), and to match the packet against one or more ACLs (standard or extended). Use the vlan filter access-map-name vlan-list vlan-list global configuration command to apply a VLAN map to one or more VLANs. A single access-map can be used on multiple VLANs.
QUESTION NO: 17
What is true about access control on bridged and routed VLAN traffic? (Select three)
A. Router ACLs can be applied to the input and output directions of a VLAN interface.
B. Bridged ACLs can be applied to the input and output directions of a VLAN interface.
C. Only router ACLs can be applied to a VLAN interface.
D. VLAN maps and router ACLs can be used in combination.
E. VLAN maps can be applied to a VLAN interface
Answer: A,B,D
Explanation:
Router ACLs are applied on interfaces as either inbound or outbound.
To filter both bridged and routed traffic, VLAN maps can be used by themselves or in conjunction with router ACLs.
VLAN ACLs, also called VLAN maps, which filter both bridged and routed packets. VLAN maps can be used to filter packets exchanged between devices in the same VLAN.
QUESTION NO: 18
Refer to the exhibit. What is the problem with this configuration?
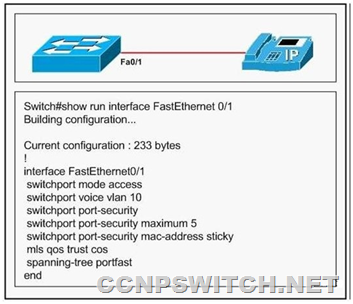
A. Spanning tree PortFast cannot be configured on a port where a voice VLAN is configured.
B. Sticky secure MAC addresses cannot be used on a port when a voice VLAN is configured.
C. Spanning tree PortFast cannot be configured on a port when a sticky secure MAC address is used.
D. The switch port must be configured as a trunk.
Answer: B
Explanation:
These are the voice VLAN configuration guidelines according to Cisco:
You should configure voice VLAN on switch access ports.
The voice VLAN should be present and active on the switch for the IP phone to correctly communicate on the voice VLAN.
The Port Fast feature is automatically enabled when voice VLAN is configured. When you disable voice VLAN, the Port Fast feature is not automatically disabled.
When you enable port security on an interface that is also configured with a voice VLAN, you must set the maximum allowed secure addresses on the port to at least two plus the maximum number of secure addresses allowed on the access VLAN. When the port is connected to a Cisco IP phone, the IP phone requires up to two MAC addresses. The address of the IP phone is learned on the voice VLAN, and it might or might not be learned on the access VLAN. Connecting a PC to the IP phone requires additional MAC addresses.
If any type of port security is enabled on the access VLAN, dynamic port security is automatically enabled on the voice VLAN.
You cannot configure port security on a per-VLAN basis.
You cannot configure static secure or sticky secure MAC addresses on a voice VLAN.
QUESTION NO: 19
Refer to the exhibit. The web servers WS_1 and WS_2 need to be accessed by external and internal users. For security reasons, the servers should not communicate with each other, although they are located on the same subnet. The servers do need, however, to communicate with a database server located in the inside network. What configuration will isolate the servers from each other?

A. The switch ports 3/1 and 3/2 will be defined as secondary VLAN community ports. The ports connecting to the two firewalls will be defined as primary VLAN promiscuous ports.
B. The switch ports 3/1 and 3/2 and the ports connecting to the two firewalls will be defined as primary VLAN promiscuous ports.
C. The switch ports 3/1 and 3/2 and the ports connecting to the two firewalls will be defined as primary VLAN community ports.
D. The switch ports 3/1 and 3/2 will be defined as secondary VLAN isolated ports. The ports connecting to the two firewalls will be defined as primary VLAN promiscuous ports.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Service providers often have devices from multiple clients, in addition to their own servers, on a single Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) segment or VLAN. As security issues proliferate, it becomes necessary to provide traffic isolation between devices, even though they may exist on the same
Layer 3 segment and VLAN. Catalyst 6500/4500 switches implement PVLANs to keep some switch ports shared and some switch ports isolated, although all ports exist on the same VLAN.
The 2950 and 3550 support “protected ports,” which are functionality similar to PVLANs on a perswitch basis.
A port in a PVLAN can be one of three types:
Isolated: An isolated port has complete Layer 2 separation from other ports within the same PVLAN, except for the promiscuous port. PVLANs block all traffic to isolated ports, except the traffic from promiscuous ports. Traffic received from an isolated port is forwarded to only promiscuous ports.
Promiscuous: A promiscuous port can communicate with all ports within the PVLAN, including the community and isolated ports. The default gateway for the segment would likely be hosted on a promiscuous port, given that all devices in the PVLAN will need to communicate with that port.
Community: Community ports communicate among themselves and with their promiscuous ports.
These interfaces are isolated at Layer 2 from all other interfaces in other communities, or in isolated ports within their PVLAN.
QUESTION NO: 20
As the network technician at Company, you need to configure DHCP snooping on a new switch.
Which three steps are required? (Select 3)
A. Configure the switch to insert and remove DHCP relay information (option-82 field) in forwarded DHCP request messages.
B. Configure DHCP snooping globally.
C. Configure the switch as a DHCP server.
D. Configure DHCP snooping on an interface.
E. Configure all interfaces as DHCP snooping trusted interfaces.
F. Configure DHCP snooping on a VLAN or range of VLANs.
Answer: B,D,F
Explanation:
When you configure DHCP snooping on your switch, you are enabling the switch to differentiate untrusted interfaces from trusted interfaces. You must enable DHCP snooping globally before you can use DHCP snooping on a VLAN. You can enable DHCP snooping independently from other DHCP features.

❓
For question number 17, shouldn’t the answer be A,C,D? This statement is wrong “Bridged ACLs can be applied to the input and output directions of a VLAN interface.” Assuming a “bridged ACL” is a vlan access map, i tried to apply it to a vlan interface, there is no option for this:
DLS1(config)#int vlan 10
DLS1(config-if)#v?
% Unrecognized command
DLS1(config-if)#vlan access-map
^
% Invalid input detected at ‘^’ marker.
DLS1(config-if)#ip access-group ?
IP access list (standard or extended)
IP expanded access list (standard or extended)
WORD Access-list name
DLS1(config-if)#ip access-group
❓